-
- SHOP
- Pool Ramp for Dogs
- For People
- For Pets
- Gallery
- Blog
- Our Company
- Cart
- Login
- Newsletter
- Free US Shipping on orders over $79!
As devoted pet parents, we understand the immeasurable joy that dogs bring to our lives. Their wagging tails and unconditional love make them cherished members of our families. However, just like us, our four-legged friends are not immune to health challenges, and one of the most prevalent concerns is joint issues.
From the exuberant puppy stages to the golden years of seniority, dogs can experience a range of joint-related problems that may affect their mobility and overall well-being. Whether your furry friend is a playful pup or a wise old soul, it’s crucial to be proactive in preventing and remedying joint issues to ensure they lead a happy and active life.
In this blog, we will delve into the world of common joint problems in dogs, exploring their causes, symptoms, and, most importantly, practical strategies to prevent and remedy these issues. Whether you have a spirited young pup or a seasoned canine companion, our aim is to empower you with knowledge and actionable insights to keep those tails wagging.
So, what are these conditions? How do they affect your dog, and more importantly, how can you treat or prevent them? In the following sections, we’ll explore just that. Before we move on, however, we want to note that all joint conditions should be diagnosed by a veterinarian, and if you suspect your dog may be struggling with one, you should schedule an appointment as soon as possible.
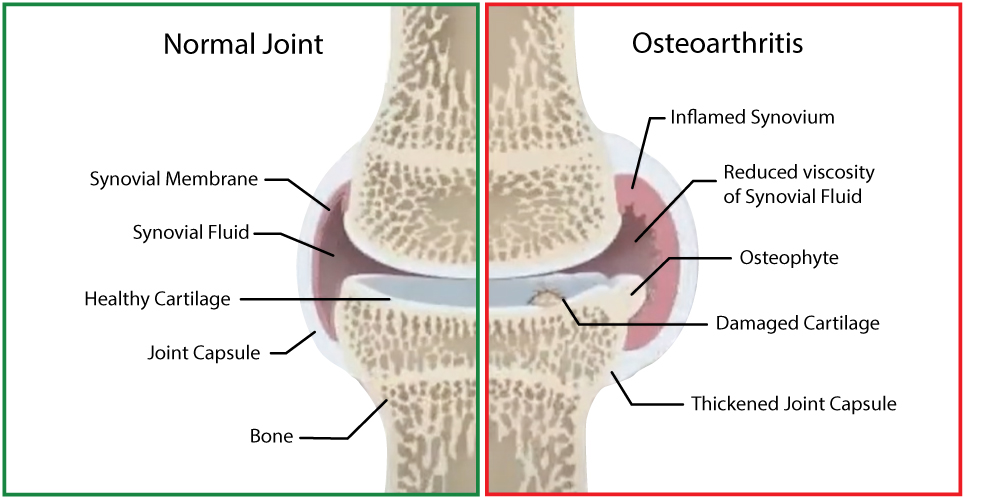
Osteoarthritis can affect dogs of varying ages but is most common in older dogs. It is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage in the joints in various parts of the body like the hips, legs, and spine.

Causes: While not always entirely known, the cause or catalyst of your dog developing osteoarthritis can stem from older age, genetic predisposition, joint instability caused by hip dysplasia or other joint conditions, joint injuries, obesity, lack of exercise, and poor nutrition.
Symptoms: Lethargy, lameness or altered gait, stiffness, difficulty rising or laying down, reluctance to exercise, pain and sensitivity, swollen joints, muscle atrophy, and overall changes in behavior like increased aggression.
Treatment: The treatment for osteoarthritis in dogs typically involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at managing pain, reducing inflammation, improving joint function, and enhancing the overall quality of life. This can include pain relief medications, physical therapy, weight management, prescription diets, corticosteroid injections, and sometimes surgery.
Hip dysplasia is a hereditary condition where the hip joint doesn’t develop properly. It is characterized by abnormal development of the hip joint, leading to instability and eventual degeneration of the joint tissues.

Causes: Genetic predisposition is a significant factor in the development of hip dysplasia. Dogs with parents or ancestors affected by hip dysplasia are more likely to inherit the condition. Certain breeds are also more prone to hip dysplasia. Large and giant breeds, such as German Shepherds, Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, and Saint Bernards, are commonly affected. However, smaller breeds can also develop hip dysplasia.
Symptoms: Hind limb lameness, difficulty rising or laying down, bunny-hopping gait, reluctance to use stairs, swaying or wobbling, and difficulty with endurance during physical activity.
Treatment: Weight management, low-impact exercise, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain management medications, prescription diet, and sometimes hip replacement surgery.
Similar to hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia is a developmental orthopedic condition that affects the elbow joint in dogs. It is characterized by abnormalities in the growth and formation of the structures that make up the elbow joint, leading to joint instability and subsequent degeneration.
Causes: Genetic predisposition is a key factor in the development of elbow dysplasia. The condition tends to occur more frequently in certain breeds, suggesting a hereditary component. Breeds commonly affected include large and giant breeds such as German Shepherds, Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, and Bernese Mountain Dogs. Rapid growth and weight gain can also contribute to your dog developing elbow dysplasia.
Symptoms: Lameness, reluctance to bear weight, stiffness, decreased range of motion, pain or discomfort, swelling of the elbow joint, cracking or popping sound during movement, and difficulty rising or lying down.
Treatment: Pain management medication, weight management, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, and surgical options to repair the joint.
Cruciate ligament injuries in dogs refer to damage or rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL), which is equivalent to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in humans. The cruciate ligaments are located within the knee joint and play a crucial role in stabilizing the joint during movement.
Causes: Trauma such as a fall, collision, or sharp twist of the knee joint, genetic factors/breed disposition, obesity, and vigorous activities.
Symptoms: Lameness, swelling and warmth around the knee joint, discomfort, stiffness, reduced range of motion, change in gait, joint instability, and difficulty rising or sitting.
Treatment: Most cases of CCL injuries in dogs will require surgical intervention, but some milder cases (usually in small dogs) do not and can be treated with exercise restriction followed by physical therapy.
Preventing joint issues in dogs involves a combination of proactive measures aimed at maintaining joint health throughout their lives. While these are key suggestions for improving joint health, if your dog is experiencing joint issues, it is essential to work closely with your veterinarian to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your dog’s specific condition and needs.
Weight management plays a crucial role in preventing joint issues and promoting overall joint health in dogs. Maintaining a healthy weight is especially important for breeds that are prone to orthopedic conditions. Excess body weight places additional stress on the joints, particularly weight-bearing joints such as hips, knees, and elbows. This increased load can contribute to the breakdown of cartilage and the development of joint issues. Keeping your dog at a healthy weight can significantly reduce the stress put on their joints and even delay the onset of joint conditions.
Making sure you are feeding your dog the proper amount of food (not too many treats!) and giving them regular physical activity can help them stay at a healthy weight.
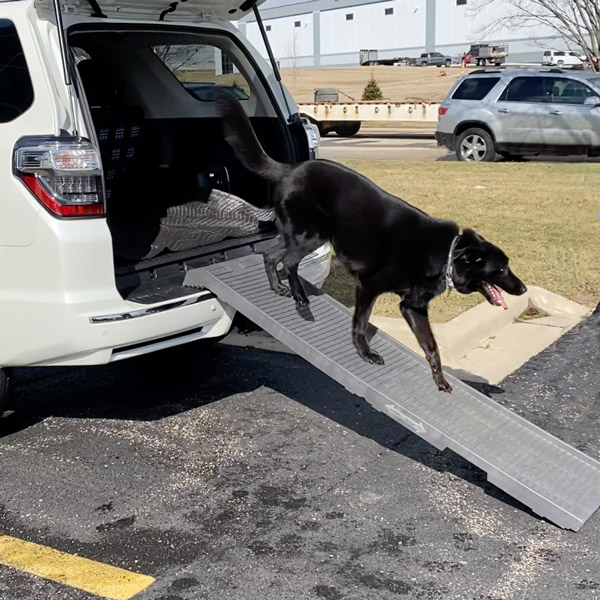

One of the best ways to minimize pain from joint damage in dogs is by using a pet ramp. Jumping on and off furniture, beds, or vehicles can place significant stress on a dog’s joints, especially the hips and knees. The Vet Record journal found that repeatedly jumping in and out of cars puts significant stress on a dog’s joints, exasperating or potentially leading to degenerative joint conditions. A pet ramp, like the PetStep ramp, provides a gentle incline, reducing the impact on joints and minimizing the risk of injury or exacerbation of existing joint issues.
In fact, co-author of the Vet Record study and Veterinary Science expert at Hartpury University Centre, Dr. Alison Wills, recommends that “people should consider using ramps stretching from their car to the ground for all dogs, [and not just] for those with existing joint problems.”
Whether used indoors or outdoors, the PetStep ramp can be a versatile solution for providing joint-friendly access to various surfaces. This adaptability allows dogs to navigate their environment with reduced strain on their joints.
Regular, controlled exercise is essential for preventing joint issues in dogs and maintaining overall musculoskeletal health. Consistent exercise promotes joint flexibility, strengthens supporting muscles, prevents stiffness, enhances bone health, and promotes circulation, reducing the risk of joint problems.
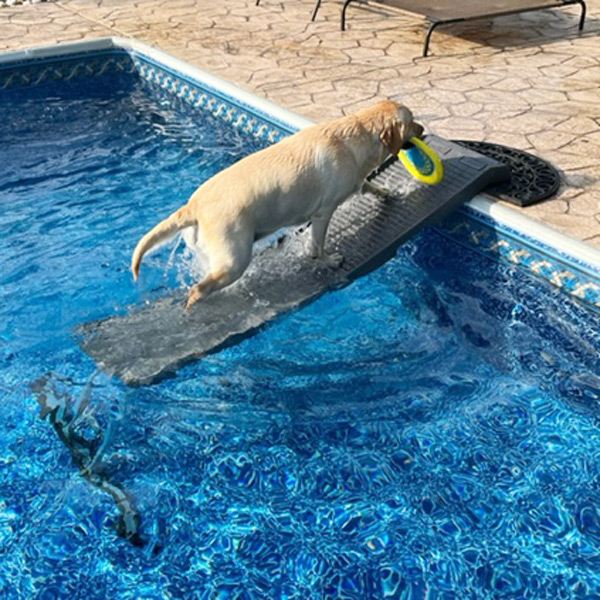

Low-impact exercise is generally the best choice for preventing and treating joint issues in dogs. This includes walking, controlled play, and swimming. If you’re lucky enough to have access to a pool, your dog can enjoy a dip that both eases and strengthens the joints. However, it may be difficult for them to enter the pool because ladders weren’t made for paws. Luckily, the PetStep pool ramp creates a gentle slope for your pup to access the pool.
Overall, it’s important to tailor the exercise routine to the individual needs, age, and health status of your dog. Consultation with a veterinarian can help design an exercise plan that suits your dog’s specific requirements and contributes to the prevention of joint issues.
By adapting your dog’s diet and adding a few supplements, you can provide essential nutrients that support joint health, manage inflammation, and contribute to your pup’s overall well-being. Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation can contribute to joint issues and arthritis, and a diet rich in omega-3s can help mitigate these inflammatory processes.
Adequate levels of calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone health. Proper bone development and maintenance reduce the risk of developmental orthopedic conditions, such as hip dysplasia.
Certain nutrients, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, are integral components of cartilage, the connective tissue that cushions joints. Including these supplements in the diet can support the structure and function of cartilage, helping to prevent degradation.
While the additions above may be beneficial to your pup’s joint health, it’s important to note that a new supplement should not be introduced without the guidance of your veterinarian.

Because our beloved canine companions bring immeasurable joy and warmth to our lives, it’s our responsibility to ensure their well-being, particularly when it comes to joint health. As we’ve explored in this blog, common joint problems such as hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and osteoarthritis can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. However, the good news is that proactive measures can be taken to prevent these issues and promote lasting joint health.
From maintaining a healthy weight and providing balanced nutrition to incorporating regular, controlled exercise and employing measures like pet ramps to reduce joint stress, the keys to prevention are within our reach. Additionally, regular veterinary check-ups are vital, serving as proactive checkpoints to catch any emerging issues and adjust preventive strategies accordingly.
By arming ourselves with knowledge and staying attuned to our furry friends’ needs, we can ensure our dogs experience the full spectrum of joy, playfulness, and comfort, unencumbered by the limitations of joint problems.